Network: Port forwarding Guide
This page explains what port forwarding is, why you need it, and how to do it.Source-Connect version 3 needs two UDP ports forwarded to the computer you are running the software on. Source-Live and Source-Nexus do not need any ports. Source-Connect 4 is optional. Additional network configuration may be required depending on your corporate network.
Whether you need to do port-forwarding at all depends on the software version you have and your network set-up: contact our support team if you have any questions.
- Contact the support team or book a session: contact support
- Source-Connect Network Guide
- Service for automatic firewall traversal: Source-Stream
- Router support: notes on specialised router support
- Port forwarding: step-by-step port forwarding guide
Follow the Guides
Almost every router variant is listed with step-by-step pictures by the good people at OpenMyIP.com and PortForward.com. If you can't find your router model here or need assistance, book a support session.
We do not endorse third-party products or guarantee that any solutions advertised by the companies linked herein will work for every user and situation. Please contact our support department if you need help or advice with port forwarding.
Test your Ports
Source-Connect Standard
When you login, Source-Connect Standard automatically tests the ports. The port status is listed under the receive level meter toward the right side of the window. To re-test ports, log out and back in.
Source-Connect Pro
Under Settings, you can test the ports by clicking the port test button, located under the Receive settings. The test result will show directly to the left of the button after the test completes.
Results
You may see any of the following results, here is what each result indicates.
- Successful/Open: The software is able to receive data properly over these ports.
- UPnP/PMP: The network is automatically mapping ports. Re-test the ports to verify it is working, and it should switch to successful/open. If not, you can try restarting the router in case it is not functioning correctly. Or, the ports may need to be manually mapped - this is usually the case when you have more than one router.
- Not mapped: The ports will need to be manually mapped. With Source-Connect, there is usually still an 80-90% success rate even without having ports mapped.
- Failed/unavailable: The ports will need to be manually mapped. This result means a successful connection is not likely.
What is Port Forwarding and why do I need it?
Source-Connect makes a certain type of connection over the internet which requires both ends of the connection, i.e. you and the person you are connecting to, to be able to see each other directly. Think of it like line of sight: You may have a firewall or anti-virus software, which is blocking the view from your computer to your connection partners. So, what we encourage you to do is configure your network to specifically create a direct line-of-sight to your computer.
Here's an example of how traffic flows when port forwarding is properly configured:
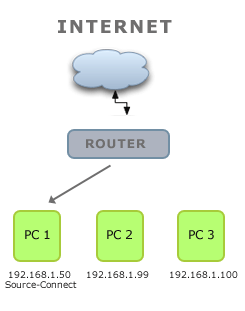
The traffic gets to the router, where it is redirected to the computer running your Source Elements software. Below is what is happening when your software can't make a connection:
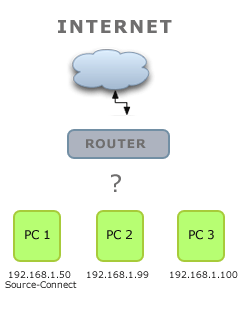
Can I make a connection with Source-Connect without "forwarded ports"?
When you try to make a connection, the internet needs to know what computer to send the data to. With most networks, we implement methods to try and make this work automatically, which works about 85% of the time in small office and home networks. In corporate or strict networks, it's likely that Source-Connect won't work at all out-of-the-box and you will need to ask your IT administrator to help. We make it easy for you to know if a connection has been established: just looking for the 'Receive' light at the top of Source-Connect. It should be blinking yellow. If it's not blinking, it means that your network, firewall or Anti-Virus program has put a block on the network.
Why does Port Forwarding guarantee a connection?
Port forwarding is a way of guaranteeing that Source Elements software can make a connection. Think about your network: you have a Cable or DSL modem/router which connects to the internet, and one or more computers connected to that modem/router. The router has a PUBLIC IP address which any computer on the internet can see. Your computers connect internally to that router and have a PRIVATE IP address. Your internal network is protected and hidden from the public internet, which means that other computers usually can't find you. So, port forwarding is a way of specifically letting the internet find certain services on your computer, for example Source-Connect, while protecting your computer from the internet in general.
How does Port Forwarding work?
On your router you can specify what happens when traffic comes in directed to a specific port and type of protocol. Source-Connect uses the UDP protocol and by default is listening on ports 6000 and 6001. So we tell your router that whenever traffic comes in on these ports, send the data directly to the IP address of your Source-Connect computer.
Why does my computer need an internal static IP address?
Most DSL and Cable connections are through a single router. You probably connect to this router via Ethernet cable, and you don't have to worry about making any network settings manually. Your router is automatically giving you an IP address every time you restart your computer or disconnect the network. What generally happens is that the IP address your computer gives you will change, so one day you have an IP of 192.168.1.100, and the next it might be 192.68.1.101. Any port forwarding configuration you make on your router needs to be fixed to a certain IP address, so it's important that it doesn't change. That's why we walk you through the steps of configuring a Static IP address internally on your computer.
Preferring DHCP reservations over manually configured static IP
Modern routers usually have a feature called "DHCP Reservation". This is superior to setting a static IP on your computer, because you don't have to worry about your computer settings being correct all the time: the router will recognize your computer when it comes online and make sure you have the ports forwarded.
Table of Contents